Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
; Yoshida, Eiichi; Aoto, Kazumi
JNC TN9400 2000-042, 112 Pages, 2000/03
A sodium-water reaction drove from the single tube break in steam generator of FBR might overheat labor tubes rapidly under internal pressure loadings. lf the temperature of tube wall becomes too high, it has to be evaluated that the stress of tube does not exceed the material strength limit to prevent the propagation of tube rupture. This study clarified the tensile and creep properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel at ultra-high temperature which will be used in evaluation of the tube burst by sodium-water reaction. The strain rates for tensile test are from 10%/min to 10%/sec, and creep-rupture time is maximum 277sec. The range of test temperature is 700 C to 1300
C to 1300 C. The main results obtained were as follows; (1)The evaluation data on the relationship between tensile strength and strain rate and creep-rupture strength in shorter time on Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel were acquired. (2)Short-term mechanical properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel were evaluated based on the results of tensile and creep-rupture tests up to 1300
C. The main results obtained were as follows; (1)The evaluation data on the relationship between tensile strength and strain rate and creep-rupture strength in shorter time on Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel were acquired. (2)Short-term mechanical properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel were evaluated based on the results of tensile and creep-rupture tests up to 1300 C. As a result of the evaluation, recommended equation of creep-rupture strength in the short-term was proposed. (3)Tensile and creep-rupture strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel tube showed the value which was higher than the 2 1/4Cr-1Mo steel, and it was proven to have the superior properties.
C. As a result of the evaluation, recommended equation of creep-rupture strength in the short-term was proposed. (3)Tensile and creep-rupture strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel tube showed the value which was higher than the 2 1/4Cr-1Mo steel, and it was proven to have the superior properties.
Terai, Takayuki*
PNC TJ9602 97-002, 75 Pages, 1997/03
Nuclear materials are often utilized under severe conditions such as high temperature, thermal transient, irradiation, corrosion by liquid metal, particle implantation, electric field and magnetic field, and an investigation on the behavior of the materials is strongly required. However, the property change is so complicated by cooperative effects of these conditions that there have been few studies on it. This project aims to clarify degradation mechanism of ceramics under the complex conditions and to contribute to the development of new advanced ceramics and surface modification. For such purposes, (1)to clarify the change in microstructure, composition and crystal structure of ceramics, (2)to analyze the distribution and condition of radiation defects and implanted ions, (3)to measure physical properties such as electric conductivity and (4)to investigate chemical and mechanical property change due to corrosion are to be carried out. In FY 1996, compatibility of several kinds of ceramic coating materials with liquid metals such as molten lithium and lithium-lead alloy (Li17-Pb83) and electrical resistivity change of these materials in the presence of the liquid metals were investigated. As a result, most of the results were in good agreement with a thermodynamic prediction and most of the compounds maintained their high electrical resistivity even in the presence of liquid lithium and lithium-lead alloy. In addition, it was pointed out that in case of Y O
O , a complex compound (LiYO
, a complex compound (LiYO ) and a non-stoichiometric compound (Y
) and a non-stoichiometric compound (Y O
O ) were formed, which was out of the thermodynamic prediction.
) were formed, which was out of the thermodynamic prediction.
Morinaga, Masahiko*; *; *; *; Inoue, Satoshi*
PNC TJ9603 96-001, 79 Pages, 1996/03
[PURPOSE] In order to develop the frontier domain of technique for the high temperature liquid alkali metal, candidate Nb-based and Mo-based alloys are needed. They are needed to have excellent compatibility with liquid Li (max. 1200 C) and super-heat-resistance. In this study, alloy design using a d-electrons alloy theory and estimation of designed alloy were performed. [EXPERIMENTAL METHODS] (1)Workability : A bend test was carried out with the provisionally designed Mo-based alloys, but by modifying the compositions by adding intergranular strengthening elements, Ti, B, C, Hf, into them to improve the ductility. (2)Corrosion resistance to liquid Li : The provisionally desingned Nb-based alloys were immersed in liquid Li at 1200
C) and super-heat-resistance. In this study, alloy design using a d-electrons alloy theory and estimation of designed alloy were performed. [EXPERIMENTAL METHODS] (1)Workability : A bend test was carried out with the provisionally designed Mo-based alloys, but by modifying the compositions by adding intergranular strengthening elements, Ti, B, C, Hf, into them to improve the ductility. (2)Corrosion resistance to liquid Li : The provisionally desingned Nb-based alloys were immersed in liquid Li at 1200 C for three hundred hours, and the weight change due to the corrosion was measured. The corrosion surface was also analyzed using SEM and EPMA. In addition, a similar corrosion test was carried out with binary Nb-based and Mo-based alloys. (3)Embrittlement at 800
C for three hundred hours, and the weight change due to the corrosion was measured. The corrosion surface was also analyzed using SEM and EPMA. In addition, a similar corrosion test was carried out with binary Nb-based and Mo-based alloys. (3)Embrittlement at 800 C : A series of experiments such as the hardness test, X-ray analysis and microstructure observation was perfomed with the Nb-1Zr alloy which was creep-tested at 800
C : A series of experiments such as the hardness test, X-ray analysis and microstructure observation was perfomed with the Nb-1Zr alloy which was creep-tested at 800 C or 1200
C or 1200 C. Also, a Nb-1Zr alloy specimen which was not creep-tested, was used as a reference specimen. [RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS] (1)Workability : The Ti addition into the Mo-based alloys was effective in improving workability. The brittleness of Mo may be caused by the existence of oxygen in the grain boundaries, so that the formation of Ti oxides probably weakened the oxygen effect, resulting in the better workability of the alloy. However, B, C and Hf additions into Mo-based alloys never improved the workability. (2)Corrosion resistance to liquid Li : Many cracks were observed on the corroded surface of the provisionally designed Nb-based alloys despite the addition of a corrosion resistant element, Hf, into them. In paticular, such cracks were developed ...
C. Also, a Nb-1Zr alloy specimen which was not creep-tested, was used as a reference specimen. [RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS] (1)Workability : The Ti addition into the Mo-based alloys was effective in improving workability. The brittleness of Mo may be caused by the existence of oxygen in the grain boundaries, so that the formation of Ti oxides probably weakened the oxygen effect, resulting in the better workability of the alloy. However, B, C and Hf additions into Mo-based alloys never improved the workability. (2)Corrosion resistance to liquid Li : Many cracks were observed on the corroded surface of the provisionally designed Nb-based alloys despite the addition of a corrosion resistant element, Hf, into them. In paticular, such cracks were developed ...
kasahara, Naoto
PNC TN9410 95-213, 38 Pages, 1995/08
In order to evaluate thermal transient strength of welded components in nuclear plants, conventional structural design codes provide conservative strength reduction factors, which are desired to be rationalized. Author extended the generalized clastic follow-up model to evaluate main causes of strength reduction of welded joints. As main causes of strength reduction of welded joints subjected to cyclic thermal transients, attention was given to (1)Metallurgical discontinuity in which the different deformation response between base metal and weld metal can result in nonuniform stresses and strain across the weldment, (2)Structural discontinuity at penetration beads of welded joints, and (3)Degradation of Weld Metal. In order to evaluate (1) and (2) of above factors, an elastic follow-up model was successfully applied. Thermal transient strength test results provide further substantiation of the validity of the elastic follow-up model for ensuring adequate life in elevated temperature component weldments. Author applied the creep-fatigue life prediction methods based on the elastic follow-up model to evaluate test results of a welded vessel model. Proposed method was proved to be adequate through comparison of predicted damagc with observed cracks data.
; Yoshida, Eiichi;
PNC TN9410 94-262, 120 Pages, 1994/09
This study clarified the tensie properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 2.25Cr-1Mo and SUS321 steels at ultra-high temperature up to 1,200 C which will be used in analysys and evaluation of the tube burst in steam generators of fast breeder reaetors. (1)Tensile strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 2.25Cr-1Mo and SUS321 steels at 1,200
C which will be used in analysys and evaluation of the tube burst in steam generators of fast breeder reaetors. (1)Tensile strength of Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 2.25Cr-1Mo and SUS321 steels at 1,200 C were 2.5, 2,and 2.5kg/mm
C were 2.5, 2,and 2.5kg/mm , respectively. (2)The difference for tensile strength and 0.2% yeild strength between specimen heat rate and heat holding time could not be found in the present. (3)The temperatures of the tube burst at the maximum internal pressure of 150kg/cm
, respectively. (2)The difference for tensile strength and 0.2% yeild strength between specimen heat rate and heat holding time could not be found in the present. (3)The temperatures of the tube burst at the maximum internal pressure of 150kg/cm corresponding to the practical use condition were expected to be approximately 960
corresponding to the practical use condition were expected to be approximately 960 C for Mod.9Cr-1M0, 860
C for Mod.9Cr-1M0, 860 C for 2.25Cr-1Mo and 1040
C for 2.25Cr-1Mo and 1040 C for SUS321, respectively. These tests result will be reflected to evaluation of tube burst by sodium water reaction.
C for SUS321, respectively. These tests result will be reflected to evaluation of tube burst by sodium water reaction.
; ; *; *; *; Yoshida, Eiichi;
PNC TN9450 91-010, 259 Pages, 1991/10
In order to advancement in materials strength standard on elevated temperature design guide of the FBRs and evaluation method of materials strength behavior, this report are presented about the creep properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steels for steam generator, based on the R&D results obtained through the activities of material tests. Contents of the data sheet are as follows; Material : Mod.9Cr-1Mo steels (Base Metal) Plate 7 Heats (F2, F6, F7, F9, F10, NSC1, NSC2) Forging 8 Heats (F4, F5, F8, F11, VIM, ESR, F520, F550) Tube 1 Heats (F3) Test temperature : 450 650
650 C Test method : According to JIS and FBR Metallic Materials Test Method Test environment : In Air and in Sodium Number of deta : 314 points
C Test method : According to JIS and FBR Metallic Materials Test Method Test environment : In Air and in Sodium Number of deta : 314 points
; ; *; *; *; *; Yoshida, Eiichi
PNC TN9450 91-008, 38 Pages, 1991/09
In order to advancement in materials strength standard on elevated temperature design guide of the FBRs and evaluation method of materials strength behavior, this report are presented about the tensile properties of FBR grade SUS316, based on the R&D results obtained through the activities of material tests. Contents of the data sheet are as follows; (1)Material : FBR grade SUS316 (Base Metal) B7 Heat 1,000mm 1,000㎜
1,000㎜ 50mm
50mm (Plate) B8 Heat 1,000㎜
(Plate) B8 Heat 1,000㎜ 1,000mm
1,000mm 40mm
40mm (Plate) B9 Heat 1,000mm
(Plate) B9 Heat 1,000mm 1,000㎜
1,000㎜ 25㎜
25㎜ (Plate) (2)Test temperature : RT
(Plate) (2)Test temperature : RT 750
750 C (3)Test method : According to JIS and FBR Metallic Materials Test Methods (4)Number of deta : 64 points
C (3)Test method : According to JIS and FBR Metallic Materials Test Methods (4)Number of deta : 64 points
Kimura, Hidetaka; *; *; Kawasaki, Hirotsugu; Aoto, Kazumi;
PNC TN9450 91-003, 28 Pages, 1991/03
None
 280mm t)
280mm t); ; Yoshida, Eiichi;
PNC TN9410 91-099, 106 Pages, 1991/02
This stady was performed in order to confirm the influence of sampling method on Creep properties of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings which are promising as candidate materials for steam generator of large scale fast breeder reactor. This results are to be reflected on fundation of materials strength standard. Test materials are four kinds of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings (thickness:250 280mmt) such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4, F8 heats), 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V(G3 heat), 9Cr-2Mo (H6 heat) steels. Results obtained are summarized as follows. (1)In order to evaluation of fundamental material properties, creep-rupture data on three kinds of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 9Cr-2Mo and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steels was obtained up to 10,000 hours. (2)The Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel exhibited most excellent creep-rupture strength and the 9Cr-2Mo steel was the worst among the three. (3)The effect of the sampling location of specimens on creep strength was not significant for Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. But for 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel and 9Cr-2Mo steel, longer creep rupture time was observed with spcimens taken from just below the center of the surface with direction of L, and shorter creep rupture time was observed for those taken from t/2 thickness at the center with direction of Z. (4)Creep strength of 9Cr-2Mo steel was lower than that of Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4, F8)and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel. But rupture elongation and reduction of area of 9Cr-2Mo steel was greater than hat of other three materials, irrespective of the sampling location of specimens.
280mmt) such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4, F8 heats), 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V(G3 heat), 9Cr-2Mo (H6 heat) steels. Results obtained are summarized as follows. (1)In order to evaluation of fundamental material properties, creep-rupture data on three kinds of 9Cr-Mo steel forgings such as Mod.9Cr-1Mo, 9Cr-2Mo and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steels was obtained up to 10,000 hours. (2)The Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel exhibited most excellent creep-rupture strength and the 9Cr-2Mo steel was the worst among the three. (3)The effect of the sampling location of specimens on creep strength was not significant for Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel. But for 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel and 9Cr-2Mo steel, longer creep rupture time was observed with spcimens taken from just below the center of the surface with direction of L, and shorter creep rupture time was observed for those taken from t/2 thickness at the center with direction of Z. (4)Creep strength of 9Cr-2Mo steel was lower than that of Mod.9Cr-1Mo (F4, F8)and 9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V steel. But rupture elongation and reduction of area of 9Cr-2Mo steel was greater than hat of other three materials, irrespective of the sampling location of specimens.
Kasahara, Naoto; Iwata, Koji; Imazu, Akira; Horikiri, Morito; Tokura, Sunao*
PNC TN9410 90-032, 321 Pages, 1989/12
Tubesheet structures are one of the most critical portions in the LMFBR components, and also have complicated configurations. Consequently, the specialized evaluation methods are required for design of tubesheets. In the case of structural design of the prototype LMFBR "Monju", the tentative design evaluation method had been suggested. It is the purpose of this study to propose the advanced method, that can be applied to designs of condenced tubesheets and of higher temperature operating ones, which are required in the demonstration LMFBR. As a conventional design method, ASME Sec. III A-8000 is basicaly adopted in the world. A-8000, however, is the elastic design method for LWR where main loading is inner pressure. For a design of tubesheets in LMFBR, It is necessary to make A-8000 adopted to thermal stress and to develop inelastic strain calculation methods. In this study we clarified the application range of A-8000 and proposed the improved method to calculate thermal stresses. The elastic design method based on perforated palate models without A-8000 is also developed. To evaluate inelastic responses of material, the relation between inelastic strain amplifications around holes of tubesheets and ligament efficiencies is obtained in the view point of dependence of inelastic behavior on ligament efficiencies. As the results, we developed the inelastic strain concentration factor which have consistency with the general purpose high temperature design code.
*; *; Kano, Shigeki; *; *; *; *
PNC TN9410 89-096, 105 Pages, 1989/05
A series of high temperature fracture toughness tests of 9Cr type steel was put in practice on a three-year scheme in 1988, In this experimental study, Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel, 9Cr-2Mo steel and TEMPALOY SW-9(9Cr-1Mo-Nb-V) steel are tested, and fracture toughness (J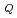 ) of base metal (As-received, SR-treated, Aged) and weldment (weld metal, HAZ) of these three types of steel are investigated. In a first year, fracture toughness tests of base metal (As-received, SR-treated) of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel were carried out at RT, 400
) of base metal (As-received, SR-treated, Aged) and weldment (weld metal, HAZ) of these three types of steel are investigated. In a first year, fracture toughness tests of base metal (As-received, SR-treated) of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel were carried out at RT, 400 C, 500
C, 500 C, 550
C, 550 C and 600
C and 600 C, respectively. In this report, the test results in the first year are shown. Fracture toughness tests were performed using R-curve method and unloading compliance method according to ASTM E813. The fracture toughness value was the lowest at 400
C, respectively. In this report, the test results in the first year are shown. Fracture toughness tests were performed using R-curve method and unloading compliance method according to ASTM E813. The fracture toughness value was the lowest at 400 C. Even at 400
C. Even at 400 C, however, Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel showed enough high fracture toughness (J
C, however, Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel showed enough high fracture toughness (J
 350kJ/m
350kJ/m ), In the fracture toughness test, tearing modurous T
), In the fracture toughness test, tearing modurous T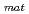 was also measured.
was also measured.
*; *
PNC TN9410 88-105, 206 Pages, 1988/04
KOM-MSS W/G studies to rationalize and revise "Elevated Temperature Structural Design Standard - Material Strength Standard - for Fast Breeder Reactor" based on new engineering techniques, knowledges of new structural materials and new evaluation method, furthermore, based on rationalized safety argorithm and design margines which have been investigated at the economical point of view. In 1987, five sub-groups organized in KOM-MSS W/G began to study on each main theme as followed. (1)1st S/G : To study material properties of Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel and its weldment at elevated temperature and to revise "Material Strength Standard (tentative in 1986)". (2)2nd S/G : To study material properties of Mod. austenitic stainless steels at elevated temperature. (3)3rd S/G : To study material properties of weldment of SUS304 at elevated temperature. (4)4th S/G : To extend the application of the usual elevated temperature structural design guide for class 1 components of prototype LMFBR. (5)5th S/G : To rationalize the evaluation method for creep-fatigue damage.